Helm (Recommended)
This is our recommended approach for deploying Sombra in production environments. While there are various ways to deploy Sombra and related components, we recommend Helm for most users, especially those with multi-cloud or hybrid cloud environments.
Prerequisites
Follow our Getting Started guide to get access to our container registry, and get all the environment variables you'll need when configuring Sombra.
Follow your hosting provider's instructions to launch a Kubernetes cluster. You should get to the point where you can connect to the cluster with kubectl.
Set up your cluster on Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS).
- Connect kubectl to EKS. On AWS, your
kubeconfigis typically configured via the aws eks update-kubeconfig command. If you used eksctl, yourkubeconfigmay have been configured automatically. - If you're setting up the LLM Classifier for Data Discovery & Classification, follow NVIDIA's guide to deploy GPU nodes on EKS.
For a complete Terraform example that creates all required AWS infrastructure, see the AWS EKS with Terraform guide.
Set up your cluster on Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS).
- Connect kubectl to AKS. On Azure, your
kubeconfigis typically configured via az aks get-credentials. - If you're setting up the LLM Classifier for Data Discovery & Classification, follow NVIDIA's guide to deploy GPU nodes on AKS.
Set up your cluster on Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE).
- Connect kubectl to GKE. On GCP, your
kubeconfigis typically configured via gcloud container clusters get-credentials. - If you're setting up the LLM Classifier for Data Discovery & Classification, follow NVIDIA's guide to deploy GPU nodes on GKE.
For on-prem deployments, you can set up your Kubernetes cluster using one of the following solutions:
- OpenShift: A Kubernetes distribution by Red Hat that provides an enterprise-ready platform with additional tools for development and operations. Follow the OpenShift Setup Guide.
- Kubeadm: A tool built to easily bootstrap a minimum viable Kubernetes cluster. It is ideal for users familiar with Kubernetes and who require granular control over their cluster configuration. Follow the Kubeadm Setup Guide.
- Rancher: An open-source platform that provides a complete Kubernetes management solution to deploy and manage clusters. Follow the Rancher Setup Guide.
- VMware Tanzu: VMware's enterprise-grade Kubernetes offering that integrates tightly with VMware infrastructure, making it suitable for environments already invested in VMware. Follow the VMware Tanzu Setup Guide.
Follow NVIDIA's guides to deploy GPUs to your Kubernetes cluster in your on premises environment.
You can test a Kubernetes cluster locally using one of these services:
Note: if you do not have an NVIDIA GPU on your machine, you will not be able to use the LLM Classifier in your cluster.
The guide you followed in Step 1 may have already set up your kubectl with your cluster's context. If so, you can proceed to Step 3.
If you haven't already installed the kubectl CLI, follow these instructions to install kubectl.
Check if your cluster's context is already available with:
kubectl config get-contextsIf you do not see your new cluster's context, you need to configure kubectl (via your kubeconfig file) to connect to your cluster. Check the documentation of your hosting provider.
- On AWS, your
kubeconfigis typically configured via the aws eks update-kubeconfig command. If you used eksctl to set up your cluster, then yourkubeconfigmay have been configured automatically. - On Azure, your
kubeconfigis typically configured via az aks get-credentials. - On GCP, your
kubeconfigis typically configured via gcloud container clusters get-credentials.
Once you have the NAME of your cluster's context (from kubectl config get-contexts), set kubectl to its context:
kubectl config use-context MY_CONTEXT_NAMEAdd Transcend's Helm repository:
helm repo add transcend https://transcend-io.github.io/helm-charts/
helm repo updateYou can list the charts available in our Helm repository with helm search repo transcend. You should see a chart for transcend/sombra.
Transcend's Helm chart repository can be found here.
Create a file named values.yaml with the following content:
imageCredentials:
password: <TRANSCEND_API_KEY>
replicaCount: 1
envs:
- name: SOMBRA_ID
value: <SOMBRA_ID>
- name: ORGANIZATION_URI
value: <ORGANIZATION_URI>
- name: TRANSCEND_URL
value: <TRANSCEND_URL>
envs_as_secret:
- name: SOMBRA_REVERSE_TUNNEL_API_KEY
value: <SOMBRA_REVERSE_TUNNEL_API_KEY>
- name: JWT_ECDSA_KEY
value: <JWT_ECDSA_KEY>
- name: INTERNAL_KEY_HASH
value: <INTERNAL_KEY_HASH>Defaults for values.yaml are set in the Helm chart's values.yaml here. Your values.yaml file overrides these defaults.
Missing some variables?
Refer to Steps 1–3 in our Getting Started guide to get the environment variables.
Now, deploy Sombra to your cluster. In Helm terms, you will install your chart onto your cluster, and each time you install, that is called a "release".
Install the sombra chart onto your cluster:
helm install sombra-test transcend/sombra --values=./values.yamlFor this test run, we've chosen the name "sombra-test" for our release. You can replace "sombra-test" with any name you'd like. The release name is used only to distinguish between several installations of the same chart in your cluster—which is not a typical situation with Sombra. It should be a lowercase string with dashes.
First, check that the Helm chart installed into your cluster:
kubectl get all --namespace="transcend"On namespaces: the chart will create a namespace in your cluster called
transcend. Most calls we'll make tokubectlrequire--namespace="transcend"(or in short form:-n transcend). Bare calls (e.g.,kubectl get all) will turn up empty results, since it's looking in the default namespace (nameddefault).Tip: Rather than type
--namespace="transcend"each time, add an alias:
alias k="kubectl --namespace=transcend"
k get all # kubectl --namespace="transcend" get all
k events # kubectl --namespace="transcend" eventsGo to the Sombra Gateways page and click the "Test" button under "Test Gateway Connection" to make a GET request to the /test endpoint of the Sombra Gateway.
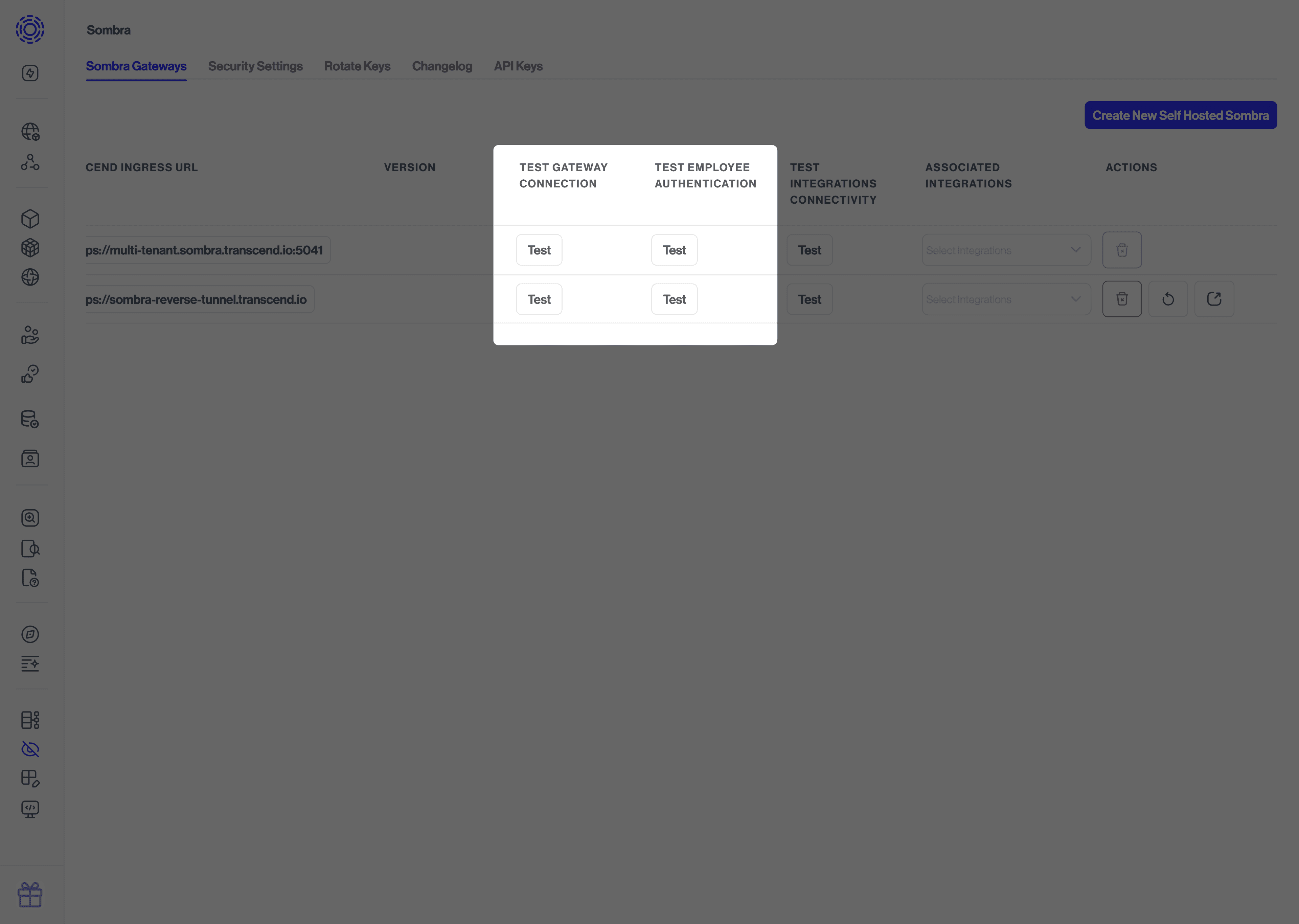
You should see a successful message if the connection is working. Congratulations on successfully deploying Sombra!
The Customizing Sombra guide covers all options available, but we recommend:
- Giving your systems access to the Sombra API through the Customer Ingress.
- Deploying the LLM Classifier, if you're using Sombra for Data Discovery & Classification.
- Setting up SSO for your admin users.
If you encounter issues during deployment, follow these steps:
1. Diagnose the issue using Kubernetes events and logs:
kubectl events -n transcend
kubectl logs -n transcend deployment/sombra-test2. Fix the issue based on the error messages (see common issues below)
3. Upgrade the release with your changes:
helm upgrade sombra-test transcend/sombra --values=./values.yamlYou don't have access to our Docker registry. Make sure you have a valid API key under imageCredentials.password in your values.yaml file. See our Getting Started guide to get the API key. If the issue persists, reach out to Transcend support.
$ kubectl events -n transcend
LAST SEEN TYPE REASON OBJECT MESSAGE
6m44s Warning Failed Pod/sombra-test-559b7796b9-j7r2w Failed to pull image "docker.transcend.io/sombra:latest": Error response from daemon: error parsing HTTP 403 response body: no error details found in HTTP response body: "{\"Message\":\"User is not authorized to access this resource with an explicit deny\"}\n"$ kubectl events -n transcend
LAST SEEN TYPE REASON OBJECT MESSAGE
27m (x2 over 32m) Warning FailedScheduling Pod/sombra-test-llm-classifier-5c9486974b-drq9v 0/1 nodes are available: 1 Insufficient memory. preemption: 0/1 nodes are available: 1 No preemption victims found for incoming pod.You need to increase the memory in your cluster.
$ kubectl events -n transcend
LAST SEEN TYPE REASON OBJECT MESSAGE
37m Warning FailedScheduling Pod/sombra-test-llm-classifier-5c9486974b-drq9v 0/1 nodes are available: 1 Insufficient nvidia.com/gpu. preemption: 0/1 nodes are available: 1 No preemption victims found for incoming pod.You're using the LLM Classifier, but your cluster is missing an NVIDIA GPU or does not have the relevant drivers installed. This is managed by the NVIDIA GPU Operator. Have you installed the GPU Operator into your cluster? See the NVIDIA guide for your hosting environment (linked in Step 1).
# Update the Helm repository
helm repo update
# Update the release
helm upgrade sombra-test transcend/sombra --values=./values.yaml