Google Firebase Plugins Configuration
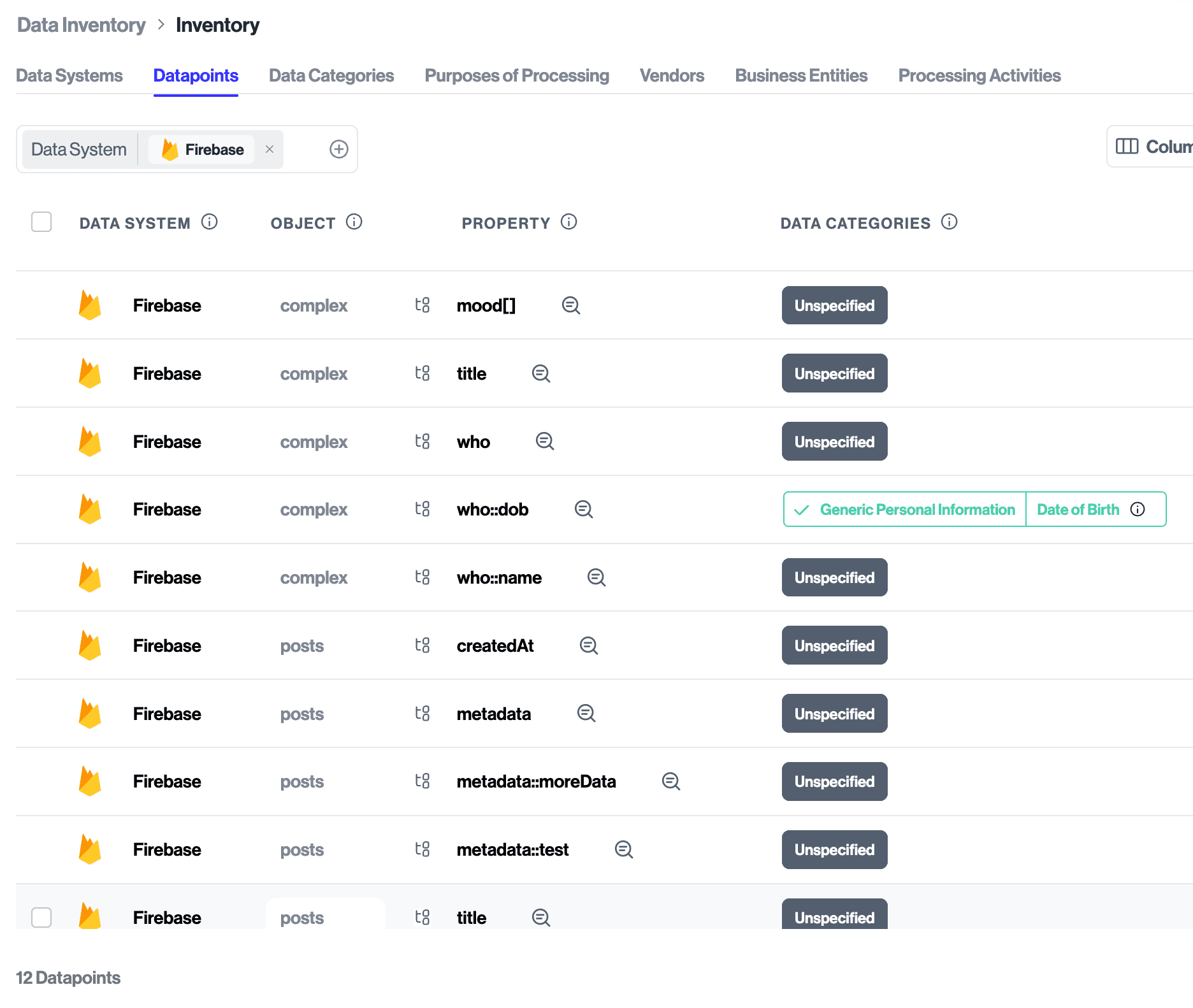
Use the Google Cloud Firestore integration with Transcend’s Structured Discovery to automatically identify personal information in your Firestore project and pull it into Transcend as datapoint. Those datapoints are assigned a data category and processing purpose to help you classify internal data. See the full Structured Discovery guide.
The Datapoint Schema Discovery plugin for Cloud Firestore scans your project to identify data and pull it into Transcend as objects and properties. Once discovered, objects and properties can be classified, labeled, and used across Transcend.
- Traversal:
- Enumerates databases in the project and lists root collections.
- Pages documents per collection (default page size 200) up to a capped number per collection, flattens document fields into canonical paths, and recursively traverses subcollections.
- Canonical path conventions (consistent across integrations):
- Nested objects/maps: use
::between path segments - Arrays: append
[]to the field name
- Nested objects/maps: use
- Subcollections are represented as nested objects in Transcend and discovered recursively.
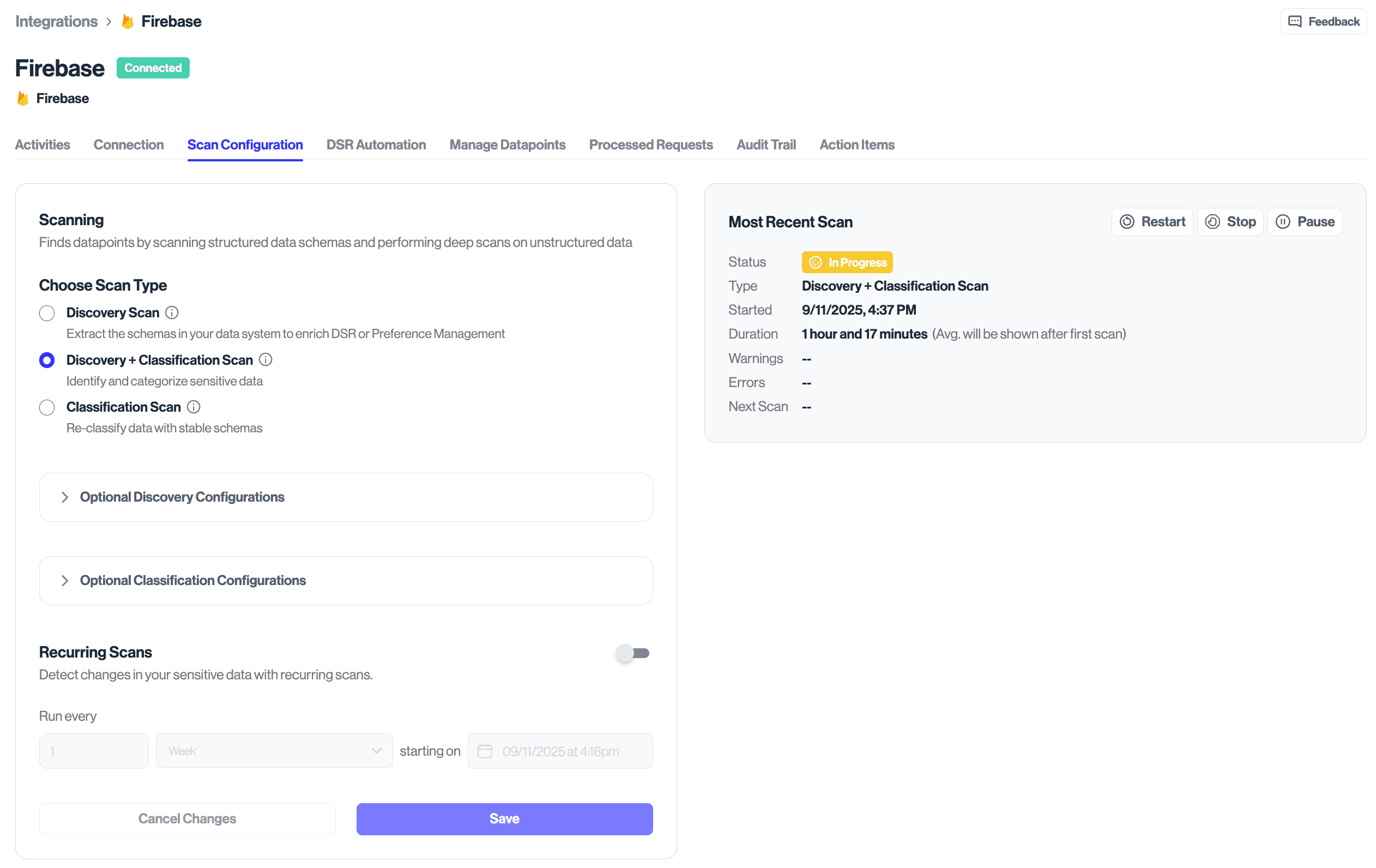
To enable the Datapoint Schema Discovery plugin, navigate to the Structured Discovery tab within the Cloud Firestore data system and toggle the plugin on. From there, set the schedule for when the plugin runs to discover new objects and properties as they are added. We recommend scheduling during off-peak hours for large datasets.
| Option | Controls | Default | Valid values | When to change | Performance impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| databaseRegexFilter | Limit scanned databases by matching the database ID (e.g.,) | Not set (no filtering) | JavaScript/ECMAScript regex string | Narrow scope in large or multi‑env projects | Fewer database enumerations; less traversal |
| databaseRegexFilterOut | Exclude databases that match the regex | Not set (false) | Boolean | Exclude test/dev, etc., with a broad regex | Faster scans; fewer API calls |
| collectionRegexFilter | Limit scanned collection paths (root and subcollections); regex matches path (e.g., /users, /users/{doc}/orders) | Not set (no filtering) | JavaScript/ECMAScript regex string | Focus on critical namespaces or avoid archival/analytics | Fewer listings and document pages |
| collectionRegexFilterOut | Exclude collection paths that match the regex | Not set (false) | Boolean | Exclude logs/events/cache without enumerating includes | Reduces traversal and sampling |
Content Classification uses samples of Firestore data to suggest data categories and processing purposes for discovered fields.
The sampling strategy determines how documents are selected for classification within a collection.
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| default | Random sampling across documents. |
| newest | Sort by a specified field descending (e.g., createdAt). |
| Option | Controls | Default | Valid values | When to change | Performance impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sampleSize | Documents sampled per collection for classification | 25 | Positive integer | Increase for priority collections that need more coverage; decrease to cut time/cost | Higher → more coverage and cost; lower → faster runs |
| pageSize | Documents per API call when listing during sampling | 500 (clamped 1–1000) | 1–1000 | Increase to reduce round‑trips; decrease if timeouts/payload/quota | Higher → fewer requests, larger responses; lower → steadier load |
| maxPages | Maximum pages fetched per collection | Not set (optional cap) | Positive integer | Set to bound runtime/quota during large scans | Lower caps reduce requests; may limit coverage |
| maxDocsTraversed | Cap on total documents traversed across sampling | Typically up to ~25,000 | Positive integer | Use to cap cost/time on large datasets | Directly bounds total work; too low may under‑sample |
| nonNullSampling | Sample only non‑null values for the target field | Disabled (unless enabled) | Boolean | Enable to avoid empty/null values skewing results | Fewer samples; higher signal per request |
| flattenMaxDepth | Max nesting depth to flatten during classification | 5 | Positive integer | Increase to include deeper leaf fields; decrease to curb cardinality | Higher depth increases derived properties/time |
| flattenMaxPathLength | Max characters for a canonical flattened path | 100 | Positive integer | Decrease to curb extremely long keys; increase if legitimate fields are dropped | Shorter limits reduce memory/output |
- Canonical path rules (aligned with Mongo): nested objects use
::(e.g.,profile::location::lat); arrays append[](e.g.,tags[],posts[]::title). - Note: When using the “newest” strategy, set
newestSortFieldto a sortable timestamp (e.g.,createdAt).
- Start with defaults, then:
- Use include/exclude filters first to bound scope (databases/collections).
- If runs are slow or quota‑heavy, lower maxDocumentsPerCollection and pageSize; consider caps on maxCollectionsPerDatabase and maxSubCollectionsPerDocument.
- For very nested schemas, set flattenMaxDepth (e.g., 3–5) to avoid an explosion of derived properties; optionally cap flattenMaxPathLength.
- For Content Classification, the defaults (sampleSize=25, pageSize=500 with 1–1000 clamp, flattenMaxDepth=5) balance coverage and performance; increase selectively for priority collections.
- Permission denied (403/UNAUTHENTICATED): Ensure the service account has
roles/datastore.viewerand theprojectIdis correct; verify Firestore is enabled for the project. - Invalid key JSON: Paste the full service account key JSON and preserve newlines.
- Quotas (429) or service unavailability (503): The integration automatically backs off and retries. Reduce page sizes, lower sample sizes, or schedule during off-peak hours.
- Newest strategy: Ensure your
newestSortFieldexists on documents.
Note: DSR Automation is not yet supported for Cloud Firestore.